cyxCoder
明天你会感谢今天奋力拼搏的你。
ヾ(o◕∀◕)ノヾ
AI大模型系列:(八)Assistants API
一、Assistants API介绍
Assistants API是2023年11月由ChatGPT在提供的一个工具,初衷是为了降低开发者的门槛。
能快速用Assistants API快速搭建一个原型应用。
目前Assistants API还处于测试阶段,功能可能会更新。
官方文档(需要科学上网才能查看):
- Guide: https://platform.openai.com/docs/assistants/overview
- API Reference: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/assistants
Assistants API的主要能力:
- 创建和管理 assistant(助手),每个 assistant 有独立的配置
- 支持无限长的多轮对话,对话历史保存在 OpenAI 的服务器上
- 通过自有向量数据库支持基于文件的 RAG
- 支持 Code Interpreter
- 在沙箱里编写并运行 Python 代码
- 自我修正代码
- 可传文件给 Code Interpreter
- 支持 Function Calling
- 支持在线调试的 Playground
国产模型也提供了类似Assistants API的功能:
- 百川:https://platform.baichuan-ai.com/docs/assistants-overview
- Minimax:https://platform.minimaxi.com/document/lbYEaWKRCr5f7EVikjFJjSDK?key=6671906aa427f0c8a570166b
- 智谱 GLM-4-AllTools:https://open.bigmodel.cn/dev/api#glm-4-alltools
- 讯飞星火助手:https://www.xfyun.cn/doc/spark/SparkAssistantAPI.html
- 阿里通义千问:https://help.aliyun.com/zh/model-studio/developer-reference/overview
二、 Assistants API的基本组件
2.1、Assistant(助手)
助手是创建的 AI 模型的配置实例,定义了它的能力和行为,如下是助手操作的代码示例:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
# 创建助手
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="数据分析助手",
description="帮助用户进行数据分析的AI助手",
model="gpt-4-turbo-preview",
instructions="你是一个专业的数据分析师,帮助用户处理数据相关问题",
tools=[
{"type": "code_interpreter"}, # 代码解释器
{"type": "retrieval"}, # 检索功能
],
file_ids=["file-abc123"] # 可选:关联文件
)
# 获取助手信息
assistant_info = client.beta.assistants.retrieve(assistant.id)
# 修改助手
updated_assistant = client.beta.assistants.update(
assistant.id,
name="高级数据分析助手",
instructions="新的指令..."
)2.2、Thread(对话线程)
对话线程用于维护用户与助手之间的对话历史。注意不是电脑进程线程的概念。
- Threads 里保存了对话历史,即 messages
- 一个 assistant 可以有多个 thread
- 一个 thread 可以有无限条 message(还是会被AI模型的Prompt大小限制,会丢掉旧的message)
- 一个用户与 assistant 的多轮对话历史可以维护在一个 thread 里
# 创建新线程
thread = client.beta.threads.create()
# 获取线程信息
thread_info = client.beta.threads.retrieve(thread.id)
# 删除线程
client.beta.threads.delete(thread.id)2.3、Message(消息)
消息是用户和助手中的具体交互内容,存在线程中,每个线程都有独立的Message。
# 创建用户消息
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id, # message 必须归属于一个 thread
role="user", # 取值是 user 或者 assistant。但 assistant 消息会被自动加入,我们一般不需要自己构造
content="请分析这个CSV文件中的销售数据趋势",
file_ids=["file-xyz789"] # 可选:附加文件
)
# 获取线程中的所有消息
messages = client.beta.threads.messages.list(thread.id)
# 获取特定消息
message = client.beta.threads.messages.retrieve(
thread_id=thread.id,
message_id=message.id
)2.4、Run(运行)
用 run 把 assistant 和 thread 关联,进行对话。
# 创建运行
run = client.beta.threads.runs.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant.id,
instructions="请特别注意异常数据" # 可选:额外指令
)
# 检查运行状态
run_status = client.beta.threads.runs.retrieve(
thread_id=thread.id,
run_id=run.id
)
# 等待运行完成的完整示例
import time
def wait_for_run_completion(thread_id, run_id):
while True:
run = client.beta.threads.runs.retrieve(
thread_id=thread_id,
run_id=run_id
)
if run.status == "completed":
return run
elif run.status == "failed":
raise Exception("运行失败")
time.sleep(1)完整对话流程示例:
def have_conversation():
# 1. 创建助手
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="数据助手",
model="gpt-4-turbo-preview",
instructions="你是数据分析专家",
tools=[{"type": "code_interpreter"}]
)
# 2. 创建对话线程
thread = client.beta.threads.create()
# 3. 发送消息
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
role="user",
content="我需要分析一组数据"
)
# 4. 运行助手
run = client.beta.threads.runs.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant.id
)
# 5. 等待响应
run = wait_for_run_completion(thread.id, run.id)
# 6. 获取助手的回复
messages = client.beta.threads.messages.list(thread.id)
return messages.data[0].content2.5、Run的状态
Run 的底层是个异步调用,意味着它不等大模型处理完,就返回。我们通过 run.status 了解大模型的工作进展情况,来判断下一步该干什么。
下面是状态之间的转移关系图:
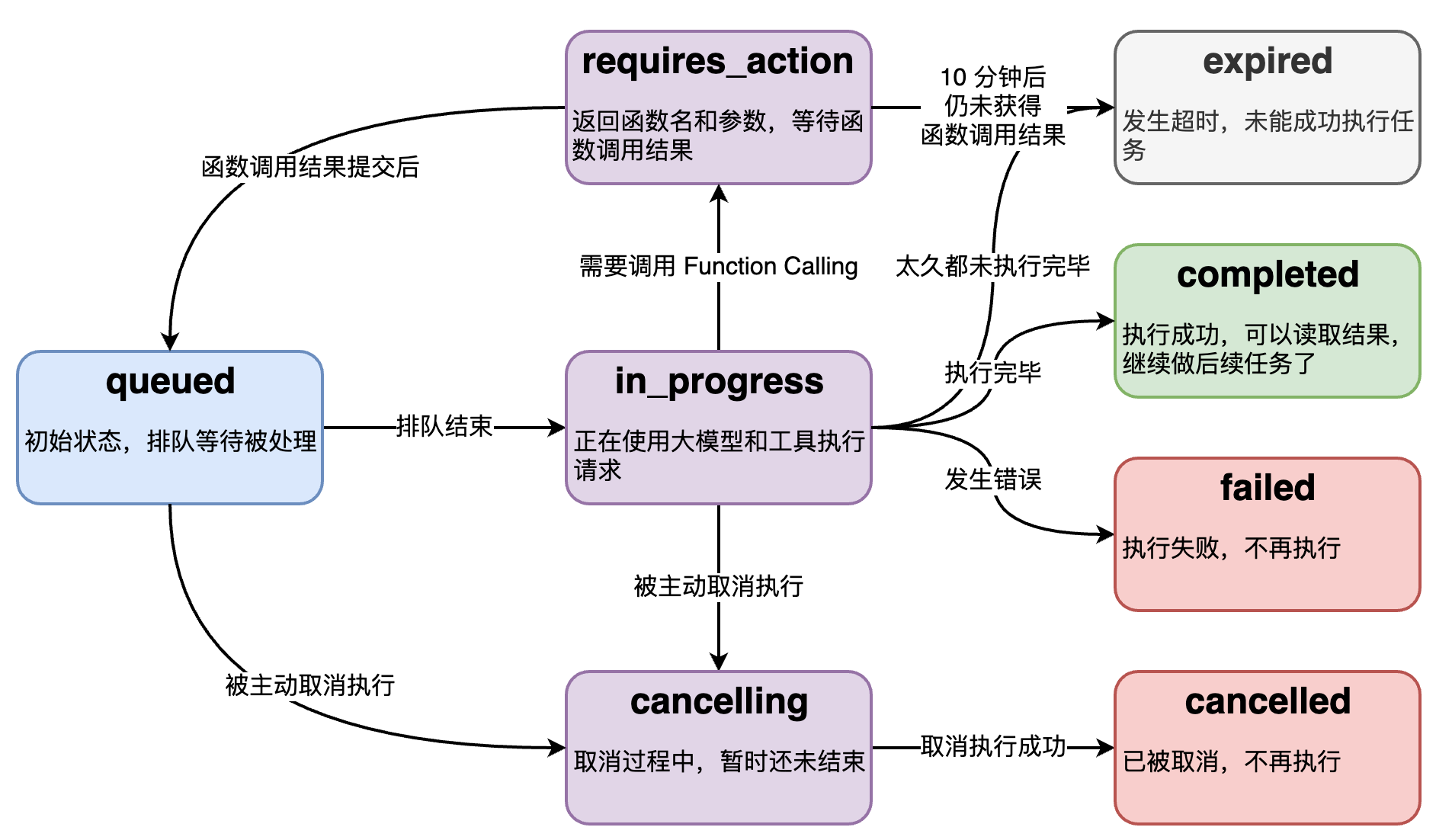
2.6、流式运行
1、创建回调函数
创建一个class继承openai的AssistantEventHandler类,重写其中的方法:
from typing_extensions import override
from openai import AssistantEventHandler
class EventHandler(AssistantEventHandler):
@override
def on_text_created(self, text) -> None:
"""响应输出创建事件"""
print(f"\nassistant > ", end="", flush=True)
@override
def on_text_delta(self, delta, snapshot):
"""响应输出生成的流片段"""
print(delta.value, end="", flush=True)2、运行run
# 添加新一轮的 user message
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
role="user",
content="你说什么?",
)
# 使用 stream 接口并传入 EventHandler
with client.beta.threads.runs.stream(
thread_id=thread.id,
assistant_id=assistant_id,
event_handler=EventHandler(),
) as stream:
stream.until_done()2.7、多个Assistants协作
其实可以多个Assistant公用一个thraed,以达到后续的Assistant可以看到之前的对话内容,这样可以达到多个Assistant之间上下文的连续性。
注意事项:
- Assistant之间仍然不能直接通信。
- 每个Run必须等待前一个Run完成。
- 需要合理设计每个Assistant和instructions,以便他们能正确理解上下文。
三、 使用Tools
3.1、code_interpreter
code_interpreter 是 Assistants API 的一个强大工具,允许 AI 助手:执行 Python 代码;处理数据分析;创建可视化;处理文件。其特别适合进行数据分析、科学计算和可视化任务。
注意事项:代码执行在沙箱环境中,有执行时间限制、内存使用限制、CPU时间限制、文件大小限制、python模块限制。
Assistants API 判断是否使用 code_interpreter 主要基于以下几个方面:
1. 显式配置
# 创建助手时明确指定使用 code_interpreter
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="编程助手",
model="gpt-4-turbo-preview",
tools=[{"type": "code_interpreter"}] # 显式启用
)2、内容识别
内容包含关键字:如数学计算、数据处理相关词语、编程语言关键字,可视化相关术语。
3、代码块识别
# 消息中包含代码块
message = """
请执行以下代码:
python
import numpy as np
x = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(x.mean())
"""
4、除了上面这些还会根据任务类型、上下文分析等手段来判断是否调用code_interpreter.
数据分析示例:
# 数据分析助手示例
def create_data_analysis_assistant():
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="数据分析助手",
instructions="""
你是一个数据分析专家,可以:
1. 读取和处理各种格式的数据文件
2. 进行统计分析
3. 创建数据可视化
4. 生成分析报告
""",
model="gpt-4-turbo-preview",
tools=[{"type": "code_interpreter"}]
)
return assistant
def analyze_data_file(file_path: str):
# 上传文件
file = client.files.create(
file=open(file_path, "rb"),
purpose="assistants"
)
thread = client.beta.threads.create()
# 发送分析请求
message = client.beta.threads.messages.create(
thread_id=thread.id,
role="user",
content="请分析这个数据文件,生成基本统计信息和可视化图表",
file_ids=[file.id]
)数学计算示例:
math_question = """
请计算以下数学问题:
1. 求解方程: x^2 + 2x - 3 = 0
2. 计算积分: ∫(x^2 + 1)dx, 从0到1
"""数据可视化示例:
visualization_request = """
使用以下数据创建一个散点图:
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y = [2, 4, 5, 4, 5]
添加标题和轴标签
"""文件处理示例:
file_processing = """
1. 读取CSV文件
2. 清理缺失值
3. 计算基本统计量
4. 生成摘要报告
"""3.2、Function Call
function call的机制在Assistants API中也能使用。
示例:
from openai import OpenAI
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
# 定义函数
def get_weather(location: str, unit: str = "celsius") -> Dict:
"""模拟天气查询功能"""
# 实际实现中会调用天气 API
return {
"location": location,
"temperature": 25,
"unit": unit,
"condition": "sunny"
}
# 函数描述
functions = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取指定位置的天气信息",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "温度单位"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
]
# 创建助手
client = OpenAI()
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
name="天气助手",
instructions="你是一个帮助查询天气的助手",
model="gpt-4-turbo-preview",
tools=[{
"type": "function",
"function": functions[0]
}]
)四、内置RAG功能
4.1、直接通过代码创建
通过代码创建 Vector Store:
vector_store = client.beta.vector_stores.create(
name="MyVectorStore"
)通过代码上传文件到 OpenAI 的存储空间:
file = client.files.create(
file=open("agiclass_intro.pdf", "rb"),
purpose="assistants"
)通过代码将文件添加到 Vector Store:
vector_store_file = client.beta.vector_stores.files.create(
vector_store_id=vector_store.id,
file_id=file.id
)批量上传文件到 Vector Store:
files = ['file1.pdf','file2.pdf']
file_batch = client.beta.vector_stores.file_batches.upload_and_poll(
vector_store_id=vector_store.id,
files=[open(filename, "rb") for filename in files]
)具体文档参考(需要科学上网):
- Vector store: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/vector-stores
- Vector store file: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/vector-stores-files
- Vector store file 批量操作: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/vector-stores-file-batches
Vector store 和 vector store file 也有对应的 list, retrieve, 和 delete 等操作(官方API:https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/files):
- client.files.list() 列出所有文件
- client.files.retrieve() 获取文件对象
- client.files.delete() 删除文件
- client.files.content() 读取文件内容
4.2、file_search
在Assistants API中RAG 实际被当作一种 tool:
assistant = client.beta.assistants.create(
instructions="你是个问答机器人,你根据给定的知识回答用户问题。",
model="gpt-4o",
tools=[{"type": "file_search"}],
)还需要指定检索源:
assistant = client.beta.assistants.update(
assistant_id=assistant.id,
tool_resources={"file_search": {"vector_store_ids": [vector_store.id]}},
)4.3、实现原理
官方文档(需要科学上网):https://platform.openai.com/docs/assistants/tools/file-search/how-it-works
内容截取:
The file_search tool implements several retrieval best practices out of the box to help you extract the right data from your files and augment the model’s responses. The file_search tool:
• Rewrites user queries to optimize them for search. (面向检索的 Query 改写)
• Breaks down complex user queries into multiple searches it can run in parallel.(复杂 Query 拆成多个,并行执行)
• Runs both keyword and semantic searches across both assistant and thread vector stores.(关键字与向量混合检索)
• Reranks search results to pick the most relevant ones before generating the final response.(检索后排序)其默认的一些配置也可以作为自己开发RAG功能的参考:
- 块大小(Chunk Size):800个tokens
- 块重叠(Chunk overlap):400个tokens
- 添加到上下文的最大块数(Maximum number of chunks added to context):20个,可能更少
五、技术选型参考
适合使用 Assistants API 的场景:
- 定制界面,或和自己的产品集成
- 需要传大量文件
- 服务国外用户,或国内 B 端客户
- 数据保密性要求不高
- 不差钱
适合使用原生 API 的场景:
- 需要极致调优
- 追求性价比
- 服务国外用户,或国内 B 端客户
- 数据保密性要求不高
适合使用国产或开源大模型的场景:
- 服务国内用户
- 数据保密性要求高
- 压缩长期成本
- 需要极致调优
六、参考资料
内容引自孙志岗老师的AI 大模型系列课程:https://agiclass.ai/
全部评论